Jihad: Concept, history and Contemporary Application
eng.dar-alifta.org/foreign/ViewArticle.aspx?ID=78
In other words, the early Quranic chapters were focused on monotheism and the ... in which God the Almighty says “Say: He is God, the only One, God the Everlasting.. He did not beget and is not begotten and none is His equal” (112: 1-4).
www.islamreligion.com › ... › Current Issues › Sects Attributed to Islam
As chapter 112 of the Quran makes clear: “He is God, the only One,. God the Everlasting. He did not beget and is not begotten, And none is His equal.” In Islam ...
The Miraculous Quran (All parts) - The Religion of Islam
www.islamreligion.com/articles/528/viewall/miraculous-quran/
By Jamaal al-Din Zarabozo (© 2007 IslamReligion.com) Published on 12 Mar 2007 - Last modified on 29 Mar 2011 ...... He begets not, nor was He begotten; And there is none co-equal or comparable unto Him” (Quran 112:1-4). ... [4] In 2 Samuel, chapter 11, verses 1-17, the leader of the Jewish people David, whom the ...
To be Muslim means to hold certain fundamental theological beliefs. The Muslim profession of faith is:
“I bear witness that there is no god but God, and I bear witness that Mohammed is a prophet of God.”
To elaborate on these statements, to be a Muslim means to believe that God is One, unique. He has no partners, no associates, no Son, nor did He ever become incarnate. As chapter 112 of the Quran makes clear:
“He is God, the only One,
God the Everlasting.
He did not beget and is not begotten,
And none is His equal.”
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
13 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
28 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
26 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
33 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
4 |
|
66 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
3 |
|
34 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
17 |
|
200 |
83 |
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
26 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
33 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
132 |
51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
17 |
|
191 |
83 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
2 |
|
13 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
3 |
|
17 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
49 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
39 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
3 |
|
19 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
28 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
49 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
88 |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
29 |
|
302 |
131 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
19 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
48 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
28 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
36 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
56 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
17 |
|
187 |
79 |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+0+9 |
|
8+0 |
Add to Reduce |
8+8+0 |
3+7+6 |
1+1+5 |
|
|
|
|
1+6 |
|
1+8 |
1+4 |
2+4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Second Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+0 |
|
|
Reduce to Deduce |
1+6 |
1+6 |
1+3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Essence of Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
13 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
28 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
26 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
33 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
4 |
|
66 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
3 |
|
34 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
38 |
|
17 |
|
200 |
83 |
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
26 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
33 |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
132 |
51 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
|
17 |
|
191 |
83 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
2 |
|
13 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
3 |
|
17 |
17 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
49 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
5 |
|
39 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
3 |
|
19 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
28 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
49 |
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
88 |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
|
29 |
|
302 |
131 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
19 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
48 |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
28 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
36 |
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
56 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
|
17 |
|
187 |
79 |
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+0+9 |
|
8+0 |
Add to Reduce |
8+8+0 |
3+7+6 |
1+1+5 |
|
|
|
|
1+6 |
|
1+8 |
1+4 |
2+4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Second Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+0 |
|
|
Reduce to Deduce |
1+6 |
1+6 |
1+3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Essence of Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
MAZE
IN
ZAZAZA ENTER ZAZAZA
ZAZAZAZAZAZAZAAZAZAZAZAZAZAZ
ZAZAZAZAZAZAZAZAZAAZAZAZAZAZAZAZAZAZ
THE
MAGIKALALPHABET
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262625242322212019181716151413121110987654321
WORK DAYS OF GOD
Herbert W Morris D.D.circa 1883
Page 22
"As all the words in the English language are composed out of the twenty-six letters of the alphabet,.."
LIGHT AND LIFE
Lars Olof Bjorn 1976
Page 197
"By writing the 26 letters of the alphabet in a certain order one may put down almost any message (this book 'is written with the same letters' as the Encyclopaedia Britannica and Winnie the Pooh, only the order of the letters differs). In the same way Nature is able to convey with her language how a cell and a whole organism is to be constructed and how it is to function. Nature has succeeded better than we humans; for the genetic code there is only one universal language which is the same in a man, a bean plant and a bacterium."
"BY WRITING THE 26 LETTERS OF THE ALPHABET IN A CERTAIN ORDER
ONE MAY PUT DOWN ALMOST ANY MESSAGE"
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
1+0 |
1+1 |
1+2 |
1+3 |
1+4 |
1+5 |
1+6 |
1+7 |
1+8 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
I |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
9 |
1+9 |
2+0 |
2+1 |
2+2 |
2+3 |
2+4 |
2+5 |
2+6 |
ME |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
1 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
1 |
"BY WRITING THE 26 LETTERS OF THE ALPHABET IN A CERTAIN ORDER
ONE MAY PUT DOWN ALMOST ANY MESSAGE"
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+0 |
1+1 |
1+2 |
1+3 |
1+4 |
1+5 |
1+6 |
1+7 |
1+8 |
1+9 |
2+0 |
2+1 |
2+2 |
2+3 |
2+4 |
2+5 |
2+6 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
|
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
"BY WRITING THE 26 LETTERS OF THE ALPHABET IN A CERTAIN ORDER
ONE MAY PUT DOWN ALMOST ANY MESSAGE"
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+0 |
1+1 |
1+2 |
1+3 |
1+4 |
1+5 |
1+6 |
1+7 |
1+8 |
1+9 |
2+0 |
2+1 |
2+2 |
2+3 |
2+4 |
2+5 |
2+6 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
|
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
HISTORY OF GOD
Karen Armstrong 1993
The God of the Mystics
THE
BOOK OF CREATION
Page 250
"THERE IS NO ATTEMPT MADE TO DESCRIBE THE CREATIVE PROCESS REALISTICALLY
THE ACCOUNT IS UNASHAMEDLY SYMBOLIC AND SHOWS GOD CREATING THE WORLD BY MEANS
OF LANGUAGE AS THOUGH HE WERE WRITING A BOOK BUT LANGUAGE HAS BEEN ENTIRELY
TRANSFORMED AND THE MESSAGE OF CREATION IS NO LONGER CLEAR EACH LETTER OF THE
HEBREW ALPHABET IS GIVEN A NUMERICAL VALUE BY COMBINING THE LETTERS WITH THE
SACRED NUMBERS REARRANGING THEM IN ENDLESS CONFIGURATIONS THE MYSTIC WEANED
THE MIND AWAY FROM THE NORMAL CONNOTATIONS OF WORDS"
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
1+0 |
1+1 |
1+2 |
1+3 |
1+4 |
1+5 |
1+6 |
1+7 |
1+8 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
I |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
9 |
1+9 |
2+0 |
2+1 |
2+2 |
2+3 |
2+4 |
2+5 |
2+6 |
ME |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
1 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
1 |
THERE IS NO ATTEMPT MADE TO DESCRIBE THE CREATIVE PROCESS REALISTICALLY
THE ACCOUNT IS SYMBOLIC AND SHOWS GOD CREATING THE WORLD BY MEANS OF LANGUAGE
AS THOUGH WRITING A BOOK BUT LANGUAGE ENTIRELY TRANSFORMED
THE MESSAGE OF CREATION IS CLEAR EACH LETTER OF
THE
ALPHABET
IS
GIVEN
A
NUMERICAL
VALUE BY COMBINING THE LETTERS WITH THE SACRED NUMBERS
REARRANGING THEM IN ENDLESS CONFIGURATIONS
THE MYSTIC WEANED THE MIND AWAY FROM THE NORMAL CONNOTATIONS OF WORDS
FINGERPRINTS OF THE GODS
A QUEST FOR THE BEGINNING AND THE END
Graham Hancock 1995
Chapter 32
Speaking to the Unborn
Page 285
"It is understandable that a huge range of myths from all over the ancient world should describe geological catastrophes in graphic detail. Mankind survived the horror of the last Ice Age, and the most plausible source for our enduring traditions of flooding and freezing, massive volcanism and devastating earthquakes is in the tumultuous upheavals unleashed during the great meltdown of 15,000 to 8000 BC. The final retreat of the ice sheets, and the consequent 300-400 foot rise in global sea levels, took place only a few thousand years before the beginning of the historical period. It is therefore not surprising that all our early civilizations should have retained vivid memories of the vast cataclysms that had terrified their forefathers.
Much harder to explain is the peculiar but distinctive way the myths of cataclysm seem to bear the intelligent imprint of a guiding hand.l Indeed the degree of convergence between such ancient stories is frequently remarkable enough to raise the suspicion that they must all have been 'written' by the same 'author'.
Could that author have had anything to do with the wondrous deity, or superhuman, spoken of in so many of the myths we have reviewed, who appears immediately after the world has been shattered by a horrifying geological catastrophe and brings comfort and the gifts of civilization to the shocked and demoralized survivors?
White and bearded, Osiris is the Egyptian manifestation of this / Page 286 /
universal figure, and it may not be an accident that one of the first acts he is remembered for in myth is the abolition of cannibalism among the primitive inhabitants of the Nile Valley.2 Viracocha, in South America, was said to have begun his civilizing mission immediately after a great flood; Quetzalcoatl, the discoverer of maize, brought the benefits of crops, mathematics, astronomy and a refined culture to Mexico after the Fourth Sun had been overwhelmed by a destroying deluge.
Could these strange myths contain a record of encounters between scattered palaeolithic tribes which survived the last Ice Age and an as yet unidentified high civilization which passed through the same epoch?
And could the myths be attempts to communicate?
A message in the bottle of time"
'Of all the other stupendous inventions,' Galileo once remarked,
what sublimity of mind must have been his who conceived how to communicate his most secret thoughts to any other person, though very distant either in time or place, speaking with those who are in the Indies, speaking to those who are not yet born, nor shall be this thousand or ten thousand years? And with no greater difficulty than the various arrangements of two dozen little signs on paper? Let this be the seal of all the admirable inventions of men.3
If the 'precessional message' identified by scholars like Santillana, von Dechend and Jane Sellers is indeed a deliberate attempt at communication by some lost civilization of antiquity, how come it wasn't just written down and left for us to find? Wouldn't that have been easier than encoding it in myths? Perhaps.
Nevertheless, suppose that whatever the message was written on got destroyed or worn away after many thousands of years? Or suppose that the language in which it was inscribed was later forgotten utterly (like the enigmatic Indus Valley script, which has been studied closely for more than half a century but has so far resisted all attempts at decoding)? It must be obvious that in such circumstances a written / Page 287 / legacy to the future would be of no value at all, because nobody would be able to make sense of it.
What one would look for, therefore, would be a universal language, the kind of language that would be comprehensible to any technologically advanced society in any epoch, even a thousand or ten thousand years into the future. Such languages are few and far between, but mathematics is one of them - and the city of Teotihuacan may be the calling-card of a lost civilization written in the eternal language of mathematics.
Geodetic data, related to the exact positioning of fixed geographical points and to the shape and size of the earth, would also remain valid and recognizable for tens of thousands of years, and might be most conveniently expressed by means of cartography (or in the construction of giant geodetic monuments like the Great Pyramid of Egypt, as
we shall see).
Another 'constant' in our solar system is the language of time: the great but regular intervals of time calibrated by the inch-worm creep of precessional motion. Now, or ten thousand years in the future, a message that prints out numbers like 72 or 2160 or 4320 or 25,920 should be instantly intelligible to any civilization that has evolved a modest talent for mathematics and the ability to detect and measure the almost imperceptible reverse wobble that the sun appears to make along the ecliptic against the background of the fixed stars..."
"What one would look for, therefore, would be a universal language, the kind of language that would be comprehensible to any technologically advanced society in any epoch, even a thousand or ten thousand years into the future. Such languages are few and far between, but mathematics is one of them"
"WRITTEN IN THE ETERNAL LANGUAGE OF MATHEMATICS"
The Upside Down of the Downside Up

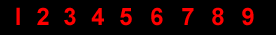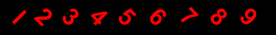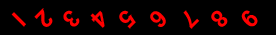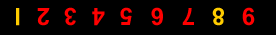
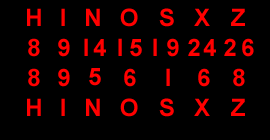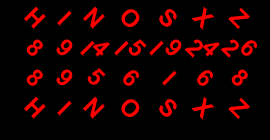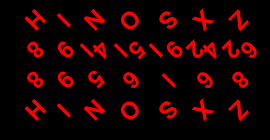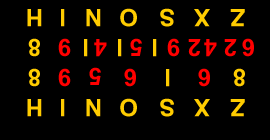










ADVENT 519 ADVENT
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
7 |
- |
1 |
|
16 |
7 |
7 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
= |
9 |
- |
1 |
|
18 |
9 |
9 |
|
= |
9 |
- |
1 |
|
9 |
9 |
9 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
19 |
10 |
1 |
- |
- |
|
- |
5 |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
2+7 |
- |
|
|
6+3 |
3+6 |
2+7 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| HIRA, HIJRAH |
| AVESTA, A, VE, STA |
| POEMANDRES, PO, EM, A, ND, R, ES |
| COSMIC, EGG |
| SIMON, MAGUS |
| THE, UNIVERSAL, MINBD, OF, GOD |
| ILLUMINATI |
| ILLUMINATI, I, L, L, U, MIN, AT, I |
| PURUSHA, SPIRIT |
| HOLY, SELF, KNOWLEDGE |
| PRIMAL, ESSENCE |
| UNIVERSE |
| THE, RIG, VEDA |
The city of Shiraz, Iran is more than 4000 years old.Shiraz - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shiraz
Two famous poets of Iran, Hafez and Saadi, are from Shiraz. Shiraz is known as the city of poets, literature, wine and flowers. It is also considered by many ...
Shirazi wine - Syrah - History of Shiraz - Shiraz County
Shiraz lies in Pars Province, a central area for Persian civilisation. The massive ruins of the Persian Empire's grand palace Persepolis, about 2500 years old, are about 60 km northeast of . Piruzapad, and Pasargadae are other nearby historic settlements.
The earliest reference to Shiraz is on Elamite clay tablets dated to 2000 BC, found in June 1970 during digging for the construction of a brick kiln in the southwest corner of the city. The tablets, written in ancient Elamite, name a city called Tiraziš.[1] Phonetically, this is interpreted as /tiračis/ or /ćiračis/. This name became Old Persian /širājiš/; through regular sound change comes the modern Persian name Shirāz. The name Shiraz also appears on clay sealings found at Qasr-i Abu Nasr, a Sassanid ruin, east of the city, (2nd century AD). As early as the 11th century several hundred thousand people inhabited Shiraz. Its size has decreased through the ages.[clarification needed]
Cuneiform records from Persepolis show that Shiraz was a significant township in Achaemenid times.[2]
There is mention of a city at Shiraz during the Sassanid era, (2nd to 6th century AD) in the 10th century geographical treatise Hudud ul-'alam min al-mashriq ila al-maghrib, which reports the existence of two fire temples and a fortress called "Shahmobad". In the 14th century the Nozhat ol-Qolub of Hamdollah Mostowfi confirmed the existence of pre-Islamic settlements in Shiraz.
Islamic period[edit]
3 |
HIRA |
|
|
|
|
HIJRAH |
|
|
|
10 |
Add to Reduce |
|
|
|
1+0 |
Reduce to Deduce |
9+0 |
6+3 |
1+8 |
1 |
Essence of Number |
9 |
9 |
9 |
6 |
AVESTA |
- |
- |
- |
|
A |
1 |
1 |
|
|
V+E |
27 |
9 |
|
|
S+T+A |
40 |
13 |
|
6 |
AVESTA |
68 |
23 |
14 |
- |
- |
6+8 |
2+3 |
1+4 |
6 |
AVESTA |
14 |
5 |
5 |
- |
- |
1+4 |
- |
- |
6 |
AVESTA |
5 |
5 |
5 |
10 |
POEMANDRES |
- |
- |
- |
|
P+O |
31 |
13 |
|
|
E+M |
18 |
9 |
|
|
A |
1 |
1 |
|
|
N+D |
18 |
9 |
|
|
R |
18 |
9 |
|
|
E+S |
24 |
15 |
|
10 |
POEMANDRES |
110 |
56 |
38 |
1+0 |
- |
1+1+0 |
5+6 |
3+8 |
1 |
POEMANDRES |
2 |
11 |
11 |
- |
- |
- |
1+1 |
1+1 |
1 |
POEMANDRES |
2 |
2 |
2 |
6 |
COSMIC |
62 |
26 |
8 |
3 |
EGG |
19 |
19 |
1 |
9 |
Add to Reduce |
|
|
|
|
Reduce to Deduce |
8+1 |
4+5 |
- |
|
Essence of Number |
|
|
|
5 |
SIMON |
70 |
25 |
7 |
5 |
MAGUS |
61 |
16 |
7 |
3 |
THE |
33 |
15 |
6 |
9 |
UNIVERSAL |
121 |
40 |
4 |
4 |
MIND |
40 |
22 |
4 |
2 |
OF |
21 |
12 |
3 |
3 |
GOD |
26 |
17 |
8 |
21 |
Add to Reduce |
|
|
|
|
Reduce to Deduce |
2+4+1 |
1+0+6 |
2+5 |
3 |
Essence of Number |
|
|
|
10 |
ILLUMINATI |
- |
- |
- |
|
I |
9 |
9 |
|
|
L |
12 |
3 |
|
|
L |
12 |
3 |
|
|
U |
21 |
3 |
|
|
M+I+N |
26 |
18 |
|
|
A+T |
21 |
3 |
|
|
I |
9 |
9 |
|
10 |
ILLUMINATI |
- |
- |
- |
7 |
PURUSHA |
104 |
32 |
5 |
6 |
SPIRIT |
91 |
37 |
1 |
H |
= |
8 |
4 |
HOLY |
42 |
24 |
6 |
S |
= |
1 |
4 |
SELF |
42 |
15 |
6 |
K |
= |
2 |
9 |
KNOWLEDGE |
96 |
42 |
6 |
6 |
PRIMAL |
69 |
33 |
6 |
7 |
ESSENCE |
70 |
25 |
7 |
T |
= |
2 |
3 |
THE |
33 |
15 |
6 |
R |
= |
9 |
3 |
RIG |
34 |
25 |
7 |
V |
= |
4 |
4 |
VEDA |
32 |
14 |
5 |
- |
- |
15 |
10 |
First Total |
|
|
|
- |
- |
1+5 |
1+0 |
Add to Reduce |
9+9 |
5+4 |
1+8 |
- |
- |
|
1 |
Second Total |
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
Reduce to Deduce |
1+8 |
- |
- |
= |
- |
|
1 |
Essence of Number |
|
|
|
THE USBORNE BOOK OF
FACTS AND LISTS
Lynn Bressler (no date)
Page 82
10 most spoken languages
Chinese 700,000,000 English 400,000,000 Russian 265,000,000 Spanish 240,000,000 Hindustani 230,000,000 Arabic 146,000,000 Portuguese 145,000,000 Bengali 144,000,000 German 119,000,000 Japanese 116,000,000
The first alphabet
The Phoenicians, who once lived where Syria, Jordan and Lebanon are today, had an alphabet of 29 letters as early as 1,700 BC. It was adopted by the Greeks and the Romans. Through the Romans, who went on to conquer most of Europe, it became the alphabet of Western countries.
Sounds strange
One tribe of Mexican Indians hold entire conversations just by whistling. The different pitches provide meaning.
The Rosetta Stone
The Rosetta Stone was found by Napoleon in the sands of Egypt. It dates to about 196 BC.
On it is an inscription in hieroglyphics and a translation in Greek. , Because scholars knew ancient Greek, they could work out what the Egyptian hieroglyphics meant. From this they learned the language of the ancient Egyptians.
Did You KnowMany Chinese cannot understand each other. They have different ways of speaking (called dialects) in different
parts of the country. But today in schools allover China, the children are being taught one dialect (Mandarin), so that one day all Chinese will understand each other.
Translating computers
Computers can be used to help people of different nationalities, who do not know each others' language, talk to each other. By giving a computer a message in one language it will translate it into another specified language.
Worldwide language
English is spoken either as a first or second language in at least 45 countries. This is more than any other language. It is the language of international business and scientific conferences and is used by airtraffic controllers worldwide. In all, about one third of the world speaks it.
Page 83
Earliest writing Chinese writing has been found on pottery, and even on a tortoise shell, going back 6,000 years. Pictures made the basis for their writing, each picture showing an object or idea. Probably the earliest form of writing came from the Middle East, where Iraq and Iran are now. This region was then ruled by the Sumerians.
The most words
English has more words in it than any other language. There are about1 million in all, a third of which are technical terms. Most
people only use about 1 per cent of the words available, that is, about 10,000. William Shakespeare is reputed to have made most use of the English vocabulary.
A scientific word describing a process in the human cell is 207,000 letters long. This makes this single word equal in length to a short novel or about 80 typed sheets of A4 paper.
Many tongues
A Frenchman, named Georges Henri Schmidt, is fluent (meaning he reads and writes well) in 31 different languages.
International language
Esperanto was invented in the 1880s by a Pole, Dr Zamenhof. It was hoped that it would become the international language of Europe. It took words from many European countries and has a very easy grammar that can be learned in an hour or two.
The same language
The languages of India and Europe may originally come from just one source. Many words in different languages sound similar. For example, the word for King in Latin is Rex, in Indian, Raj, in Italian Re, in French Roi and in Spanish Rey. The original language has been named Indo-European. Basque, spoken in the French and Spanish Pyrenees, is an exception. It seems to have a different source which is still unknown.
Number of alphabets
There are 65 alphabets in use in the world today. Here are some of them: Roman
ABCDEFGHUKLMNOPQRS Greek Russian (Cyrillic) Hebrew Chinese (examples omitted)
DAILY MAIL
Monday, October 8, 2007
Harry Bingham
Page 15
"YOU SAY POTATO, I SAY GHOUGHBTEIGHPTEAU !"
"...Yes you CAN spell potato like that. It's one of the amazing quirks which make English the world's dominant language
"ABOUT three years ago I started researching a book, This Little Britain, about the various ways in which
we Brits have a history .
of being the exception.
In areas such as law, government, economics, agriculture and science, we've often been a uniquely British exception to a general European rule.
Ditto, in such things as men's fashion, Victorian sewers, drunken yobbishness, and - not least - in the whole area of language and literature.
Take spellings. George Bernard Shaw famously commented that English spelling would allow you to write the word 'fish' as 'ghoti' - and it would sound the same (in the latter, the sound 'f' would be from 'gh', as in 'rough'; 'i' would be from 'o' in 'women' and 'sh' as in 'ti' from 'nation').
But he couldn't have been trying all that hard, if that was the best example he came up with. How about 'potato' as in
'ghoughbteighpteau'? That's the sound 'p' as in hiccough, 'o' as in
though, 't' as in debt, 'a' as in neighbour, 't' as in ptomaine, 'o' as in bureau. The fact is that with just 26 letters and 48 different sounds to cope with, there were
always going to be problems. :
Throw in other pronunciation
changes and an appetite for
foreign borrowings, and it's no surprise that English has some of
the most dangerously unpredictable spellings in the world.
If our spellings are painful, however, our grammar has its blessedly simple side. French nouns are either masculine or feminine; French verbs vary with every puff
of the syntactical breeze.
But French is a pretty simple language. Italian has 50 different forms for every verb, ancient Greek more than 300, modern Turkish an eye popping two
million. English, by contrast, has
just four verb forms (bark, barks, barking, barked), two noun forms (dog, dogs), and just one adjectival form (snappy), thus making our language about the least inflected in the world.
If that's a curious fact, the reason why is perhaps odder still. Back in Alfred the Great's England, two language communities - English and Danish - intermingled. Each community could make out the basic words of the other language.
FOR example, the word 'horse' is 'hors' in Old English, 'hossit' in Old Norse. But all those tricksy little word endings would have made no sense at all. So they began to vanish.
Under pressure of trade, friendship and intermarriage, our ancient ancestors did away with inflections almost completely. Confusing at the time, no doubt, but a blessing for those who need to learn the language today.
And there are plenty of people learning it, of course. With about one-and a-half billion non-native speakers, English has become the world's own language - one that accounts for two-thirds of internet content, and a still larger proportion of the world's scientific and technical journals.
It's sometimes suggested that English has achieved its leadership because it's thelanguage of Shakespeare, . because of its unique and beautiful literature.
That's nonsense, of course. English dominates because the British Isles exported English speakers and gunboats in the 19th century, and because America exported Hollywood, GIs and hamburgers in the 20th.
If those Mayflower settlers had
chanced to speak Ubykh (a Caucasian language with 81 consonants and 'three vowels) or Rotokas (a Papua New Guinea language with just six consonants and five vowels), the world would most likely be speaking those fine languages today.
Such dominance has its downside, of course. There are now about 6,800 languages left in the world, compared with perhaps twice that number back at the dawn of agriculture. The remaining languages are now dying at the rate of about one a fortnight.
English is big in other ways too. If you wanted to learn all the words in the Oxford English Dictionary, you'd have to deal with about 500,000 of them (ending with zyxt, a splendid last word by any standards and an archaic Kentish term for thou seest).
Having done that, you'd probably be a bit taken aback to learn the equivalent American dictionary, Webster's, offers a further 450,000 words or so, of which only about half are to be found in the OED, suggesting a pooled total word count of about 750,000.
But there are lots of words that never get in to either dictionary. Flora and fauna are mostly out. So are most acronyms, slang and
dialect. Total that lot up and
you'd get to a million or so. Next, you'd need to deal with scientific and technological terms, adding another million or so words.
Otherlanguages-can't keep up. The official dictionary-based word count of German is fewer than 200,000. The French wordcount is fewer than 100,000. The scale of our vocabulary is impossible to explain, except by recognising that English users are
reckless adopters and inventors.
In the cultural realm, however, mere size is hardly likely to impress. In tenus of Nobel Prizes for literature, the United Kingdom trots home in the bronze medal position (beaten by goldmedallist France, and the silvergong-holder, the US.).
If, on the other hand, you were looking at the total amount of literatureproduced by the British Isles then we would come in level
with France, with 13 prizes.
BUT perhaps that's to measure things the wrong way. If you look at Nobel Prizes by language, then English wins by a country mile 26 laureates vs 13 for France).
More to the point, the Nobel Prize Committee is just that: a committee. Wouldn't it be better to let the world's reading public determine which literature it favours? Alas, there are no reliable global sales figures available.
We do, however, have an index of which authors have written the most translated books. British authors romp home in four of the top five places: Agatha Christie in first, then Enid Blyton, Shakespeare and Barbara Cartland in third to fifth. (The one interloper, Frenchman Jules Verne, is in second place.)
Looking more broadly, British authors dominate the top 40, with some 14 authors on the list, compared with 11 for the United States, and 15 for the entire rest of the world put together.
The obvious conclusion: that we Brits have some natural affinity for words and literature, the way that the Germans 'do' music, or the French 'do' visual art.
Such things run both deep and
ancient. The vernacular literature of Alfred the Great's England was the most developed in Europe. It's perhaps not surprising that the same is arguably still true today."
"YOU SAY POTATO, I SAY GHOUGHBTEIGHPTEAU !"
"How about 'potato' as in
'ghoughbteighpteau'?"
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
G+H |
15 |
15 |
6 |
2 |
O+U |
36 |
9 |
9 |
2 |
G+H |
15 |
15 |
6 |
3 |
B+T+E |
27 |
9 |
9 |
1 |
I |
9 |
9 |
9 |
2 |
G+H |
15 |
15 |
6 |
2 |
P+T |
36 |
9 |
9 |
3 |
E+A+U |
27 |
9 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1+8+0 |
9+0 |
6+3 |
|
|
|
|
|
INDIA I AND I INDIA
Amazon.com Apple iBookstore Barnes & Noble
Lord Kapila is a renowned sage and the author of the philosophical system known as Sankhya, which forms an important part of India's ancient philosophical heritage.
Sankhya is a system of metaphysics that deals with the elemental principles of the universe; it is also a system of spiritual knowledge, with its own methodology, and culminates in full consciousness of the Supreme Absolute.
Lord Kapila, however, is not an ordinary philosopher or sage but an incarnation of God.
This book deals with his answers to his mother's enquiry about how to overcome ignorance and delusion and attain spiritual enlightenment.
LORD KAPILA 99-45-9 9-45-99 KAPILA LORD
KAPILA 50-23-5 5-23-50 KAPILA
DEVAHUTI 90-36-9 9-36-90 DEVAHUTI
Teachings of Lord Kapila | Krishna.com
krishna.com/books/teachings-of-lord-kapila
Lord Kapila's answers to his mother's inquiry about how to overcome ignorance and attain spiritual enlightenment. Lord Kapila is a renowned sage and the ...
Teachings of Lord Kapila
The Son of Devahuti
Lord Kapila's answers to his mother's inquiry about how to overcome ignorance and attain spiritual enlightenment.
Lord Kapila is a renowned sage and the author of the philosophical system known as Sankhya, which forms an important part of India's ancient philosophical heritage.
Sankhya is a system of metaphysics that deals with the elemental principles of the universe; it is also a system of spiritual knowledge, with its own methodology, and culminates in full consciousness of the Supreme Absolute.
Lord Kapila, however, is not an ordinary philosopher or sage but an incarnation of God.
This book deals with his answers to his mother's enquiry about how to overcome ignorance and delusion and attain spiritual enlightenment.
The underlying theme running throughout his answers and throughout Srila Prabhupada's commentaries on them is that one can achieve this goal by practicing bhakti-yoga, the process of linking one's heart to the Lord's heart through loving devotional service.
This series, with original Sanskrit, translations, and purports, sheds light on such topics as the significance of the guru, the psychology of consciousness, the characteristics of a self-realized person, the science of meditation, the nature of transcendental knowledge, and the process of ultimate liberation.
THE GUINNESS ENCYCLOPEDIA
John Foley
1993
ALPHABETOLOGY
SIGNS AND SYMBOLS
Page 22
The most commonly used numerical symbols throughout the modern World; the so-called Arabic numerals
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
derive ultimately from a system developed by the Hindus in India sometime between the 3rd Century B,C. and 6th Century A.D.
The more rounded Western Arabic numerals were introduced into Spain by the Moors in the 10th Century.
The first European to take serious note of the new numeration was the French scholar Gerbert of Aurilliac (Pope Sylvester II from 999 to 1003) who had studied the system in Spain
The Hindus are also credited with the invention at some unknown date of the symbol for zero, which was first written as a small circle and later reduced to a large dot.
The nine Indian figures are : 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
With these nine figures and with the sign O any number may be written.
Leonardo of Pisa
Liber abaci
1234 5 6789
ONE TWO THREE FOUR 5FIVE5 SIX SEVEN EIGHT NINE
1234 5 6789 9876 5 4321
NINE EIGHT SEVEN SIX 5FIVE5 FOUR THREE TEO ONE
9876 5 4321
- |
|
|
- |
- |
|
L+O |
27 |
9 |
9 |
2 |
V+E |
27 |
9 |
9 |
|
LOVE |
|
|
|
- |
|
5+4 |
1+8 |
1+8 |
|
LOVE |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
- |
- |
- |
|
|
- |
- |
- |
EVOLVE |
|
|
|
|
E+V |
27 |
9 |
9 |
|
O+L |
27 |
9 |
9 |
2 |
V+E |
27 |
9 |
9 |
|
EVOLVE |
|
|
|
- |
|
8+1 |
2+7 |
2+7 |
|
EVOLVE |
|
|
|
THE LOST LANGUAGE OF SYMBOLISM
Harold Bayley
The Lost Language of Symbolism: An Inquiry into the Origin of Certain Letters,
Words, Names, Fairy-Tales, Folklore, and Mythologies. 2 vol. 1912
Page 41
"Mysticism has universally taught that every man has within himself the germs or seeds of Divinity, and that by self-conquest these sparks of Heaven may be fanned into a flame, the flame into a fire, the fire into a star, and the star into a sun."
THE LOST LANGUAGE OF SYMBOLISM
Harold Bayley
The Lost Language of Symbolism: An Inquiry into the Origin of Certain Letters,
Words, Names, Fairy-Tales, Folklore, and Mythologies. 2 vol. 1912
INTRODUCTION
"... Although etymologists are agreed that language is fossil poetry and that the creation of every word was originally a poem embodying a bold metaphor or a bright conception, it is quite unrealised how close and intimate a relation exists between symbolism and philology. But, as Renouf points out, " It is not improbable that the cat, in Egyptian Mau, became the symbol of the Sun-God or Day, because the word Mau also means light." 1 Renouf likewise notes that not only was RA the name of the Sun-God, but that it was also the usual Egyptian word for Sun. Similarly the Goose, one of the symbols of SEB, was called a Seb ; the Crocodile, one of the symbols of SEBEK, was called a Sebek; the Ibis, one of the symbols of TECHU, was called a Techu ; and the Jackal, one of the symbols of ANPU (ANUBIS), was called an Anpu.
Parallels to this Egyptian custom are also traceable in Europe, where, among the Greeks, the word Psyche served not only to denote the Soul but also the Butterfly, a symbol of the Soul; and the word Mylitta served both as the name of a Goddess and of her symbol the Bee. Among the ancient Scandinavians the Bull, one of the symbols of THOR, was named a Thor, this being an example, according to Dr Alexander Wilder, " of the punning so common in those times, often making us uncertain whether the accident of similar name or sound led to adoption as a symbol or was merely a blunder." 2
I was unaware that there was any ancient warrant for what I supposed to be the novel supposition that in many / Page12 / instances the names of once-sacred animals contain within themselves the key to what was originally symbolised. The idea that identities of name were primarily due to punning, to blunder, or to accident, must be dispelled when we find that-as in most of the examples noted by myself -the symbolic value of the animal is not expressed by a homonym or pun, but in monosyllables that apparently are the debris of some marvellously ancient, prehistoric, almost extinct parent tongue. Modern language is a mosaic in which lie embedded the chips and fossils of predecessors in comparison with whose vast antiquity Sanscrit is but a speech of yesterday. In its glacier-like progress, Language must have brought down along the ages the detritus of tongues that were spoken possibly millions of years before the art of recording by writing was discovered, but which, notwithstanding, were indelibly inscribed and faithfully preserved in the form of mountain, river, and country names. Empires may disappear and nations be sunk into oblivion under successive waves of invasion, but place names and proper names, preserved traditionally by word of mouth, remain to some extent inviolate; and it is, I am convinced, in this direction that one must look for the hypothetical mother-tongue of the hypothetical people, known nowadays as "Aryans. "
Page 11. Notes.1 On the Origin and Growth of Religion as Illustrated by the Religion 0/
Ancient Egypt, p. 237 ; Hibbcrt Lectures, p. 879. 2 Symbolical Language of Ancient Art and Mythology, R. Payne-Knight,
P.124.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
= |
3 |
|
2 |
L |
12 |
3 |
3 |
A |
= |
1 |
|
2 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
N |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
N |
14 |
5 |
5 |
G |
= |
7 |
|
2 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
U |
= |
3 |
|
3 |
U |
21 |
3 |
3 |
A |
= |
1 |
|
3 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
G |
= |
7 |
|
4 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
E |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
E |
5 |
5 |
5 |
- |
- |
32 |
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
68 |
32 |
32 |
- |
- |
3+2 |
- |
|
- |
6+8 |
3+2 |
3+2 |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
1+4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
= |
3 |
|
2 |
L |
12 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
= |
1 |
|
2 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
N |
14 |
5 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G |
= |
7 |
|
2 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= |
3 |
|
3 |
U |
21 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
= |
1 |
|
3 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
G |
= |
7 |
|
4 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
E |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
32 |
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
68 |
32 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
3+2 |
- |
|
- |
6+8 |
3+2 |
3+2 |
|
|
|
|
|
1+0 |
|
1+4 |
|
|
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
1+4 |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
= |
3 |
|
2 |
L |
12 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
= |
1 |
|
2 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
N |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
N |
14 |
5 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
G |
= |
7 |
|
2 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
U |
= |
3 |
|
3 |
U |
21 |
3 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
A |
= |
1 |
|
3 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
G |
= |
7 |
|
4 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
E |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
E |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
32 |
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
68 |
32 |
32 |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
3+2 |
- |
|
- |
6+8 |
3+2 |
3+2 |
|
|
|
1+0 |
1+4 |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
1+4 |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L |
= |
3 |
|
2 |
L+A+N |
27 |
9 |
9 |
A |
= |
1 |
|
2 |
G+U+A+G |
18 |
18 |
9 |
N |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
E |
5 |
5 |
5 |
- |
- |
32 |
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
68 |
32 |
32 |
- |
- |
3+2 |
- |
|
- |
6+8 |
3+2 |
3+2 |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
1+4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A |
= |
1 |
|
3 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
A |
= |
1 |
|
2 |
A |
1 |
1 |
1 |
L |
= |
3 |
|
2 |
L |
12 |
3 |
3 |
U |
= |
3 |
|
3 |
U |
21 |
3 |
3 |
E |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
E |
5 |
5 |
5 |
N |
= |
5 |
|
3 |
N |
14 |
5 |
5 |
G |
= |
7 |
|
2 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
G |
= |
7 |
|
4 |
G |
7 |
7 |
7 |
- |
- |
32 |
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
68 |
32 |
32 |
- |
- |
3+2 |
- |
|
- |
6+8 |
3+2 |
3+2 |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
1+4 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
- |
8 |
LANGUAGE |
|
|
|
SOME MYSTICAL ADVENTURES
G, R, S. Mead 1910
XIII
ON THE ART OF SYMBOLISM.
Page 180
"The Mind of the Father hath sown symbols through the world."
THE CHALDAEAN ORACLES.
"MANY people talk vaguely about symbols and some are really interested in symbolism; but even of those who may happen to possess a little learning on the subject, how few are there who, if they turn and really face themselves and there is no audience to play to, can say they have got to the heart of the matter, or know how rightly to seize the proteus whose changing forms they are ever grasping at, and so force it to speak true words?
I, for my part, freely admit that I am as yet far from the real heart of the matter. I cannot yet hold the proteus steady and force it to speak true words of power; but there is joy in the game of catch-as-can-catch, and I am game for a short bout; though doubtless, as of yore, the wily one will change into something I have never thought of before, and I shall have no grip in mind to hold him.
Page 181
'Symbol' is no native name; it is a Greek importation (symbolon), and its root-meaning is said to be a sign, or token, by which one knows or infers a thing. The utterance of this word should awaken in us the idea of putting together (sym-ballein), with the notion (in the passive) of to correspond and to tally. But to put together is to compare, and so to compare one's own opinion with facts, and hence to conclude, infer, conjecture, interpret; and it is from this last meaning that, the wisdom of the word-books tells us, we get the meaning of symbol as a sign, or token, by which one knows or infers a thing.
I am afraid that we have not yet grasped our proteus amid all these changing forms of words. A symbol is a sign, but that again is a Latin importation (signum), and we may pass it by. A symbol is a token; that is good English. Token is connected with to teach, to point out, show, witness; to betoken is to be a symbol of.
But words will not help us much; they are forms of speech that are ever slipping away into other forms. A symbol is not a word; it is something more fundamental; in its proper meaning it is something almost more primitive than an ideogram, or type-picture. Let us go in search of the idea-the living idea, not some abstract inference-the fulness, not the flat.
If there is a 'flat-land' as compared with a / Page 182 / three-dimensional land, may we not think of symbol-language as a three-dimensional language, so to speak, when compared with the' flat' languages of ordinary speech? Or, to use these words in a deeper meaning, speech in its most primitive mode is action, and so symbolic action, or drama, might be said to be the true symbollanguage. This symbol - or three-dimensional language is closely connected with ceremony. And ceremony (Lat. eeremonia) is a word formed on a stem that grows from the root ere (as in creo, I make, create), which is of the same origin as the Sanskrit kri (as in karma, action, doing). A ceremony is a sacred rite; that is, it is typical, and as such should be of creative potency, for as the Chaldaean Oracle has it: "The Mind of the Father hath sown symbols through the world." That which is typical is ideal, for type and idea are synonyms.
Are we now getting any nearer the heart of the matter? Are we beginning to make our symbols alive? Can we afford to dismiss any true symbol with the dull remark: "It's only a symbol"? The universe itself is a symbol; man is a symbol.
Even in their lowest strata symbols are the ' out-lines,' so to say, of three-dimensional objects from some point of view, seen from one side or another; and' out-line' in its inner meaning is / Page 183 / intimately connected with idea; it is, as it were, a ground-plan.
Now as symbols in this sense have to do with ideas and types, are connected with the living side of things, it is not possible to interpret a symbol in one set fashion only and tie it down to one set form. We cannot make an 'exact science' of symbolism; it is initiatory rather than didactic; it 'starts' one towards living ideas, it does not peg us out in some rigid configuration.
So that if it is asked, how does one know that this or that is the right interpretation of any particular symbol, it is exceedingly difficult, if not impossible, to prove it in the way of physical demonstration. If the interpretation really fits, there will be a response within. It will be a living response; not the imprisoning of the mind in a dead form. In the interpretation of symbols we must be prepared to give up exactness, in the way it is generally understood, and allow our minds free play. At the beginning it is best to use any hint that seems to promise well; first apply it in every direction, then as soon as ever it has led to another clue, throw it away.
In learning the great language of symbols it is necessary to keep the mind ever free, plastic, and adaptable. If we persist in keeping stuck in the old ruts, we shall never learn the meaning / Page 184 / of symbols. The beauty of great symbols is the infinite variety of their modes of interpretation. To think there is only one definite interpretation for each symbol is to paralyse one's symbol-mind, and make it fall dead and flat into the superficial. One should play with symbols as a mathematician plays with numbers; symbols are the playthings of the gods. And I think the secret of interpreting symbols is to get the symbol first into one's mind, and not one's mind into the symbol.
The mind should not be allowed to relate itself to the symbol, should not allow itself to be attracted by the picture into going out of itself and crystallising itself into one form; but the symbol should rather be compelled to relate itself to the mind. It should be taken into the mind, and then the mind will be able to see it from every side and grasp it as a whole.
Symbol-language has its letters and its words, and the above may be suggested as a method of learning the alphabet. But symbol-language is not the same thing quite as symbolical language, nor is it to be confused with metaphorical language. Metaphor is transferring the meaning of one word to another in ordinary speech. It is exceedingly important, quite a mystic art, a sort of game of 'general post' among the ideas connected with words.
A metaphor gives a meaning that is not to be / Page 185 / understood literally, or according to the facevalue of the letters as we know them, but a reading of root-ideas, as it were, abstracting or subtracting the substance from them. That is to say, we take away the substance that built the idea and keep the idea, and then expand it and spread it out cosmically in every direction. Metaphors may be said to be more connected with substance, symbols with spirit.
Symbols should be ' eaten' and' digested,' so to say. Triangles and svastikas, for instance, might be said to be symbols which, when gazed upon in an ecstatic state of mind-that is, taken within and contemplated-nourish the body of essence; if made alive they create pleasing sensations in it, stimulate, feed, and excite it, rearrange all its activities, alter the currents in it and build it. All great symbols are said to do this-that is, all cosmic symbols or forms that are directly related to things-that-are. These cosmic symbols suggest modes of creative energies; when creative powers act they draw certain patterns and plans and not others; and these patterns, types, and ideas are cosmic symbols, and it is by ecstatically gazing at them, that they nourish our root-substance and so enform it cosmically, or in a harmonious or orderly fashion.
Symbols are toys in the great game. We / Page 186 / should thus learn to play with symbols in the true Kindergarten, the' everlasting revellingplace '-the essential substance that is our nursery and our cradle, and our womb for birth into greater things. But this game is a living thing; we should make symbols act; we learn little while we keep them steady. A true symbol should be ever in motion. Nor should we be satisfied till we can glide from one symbol to another. While we think of symbols as dead detached objects cut off from one another, and bearing no relation to each other, we shall know nothing. We should play with them, draw them or picture them from every standpoint, till we catch fresh glimpses every moment.
Let us think of one great world-body ever in motion; all true symbols may be said to be attempts to snapshot this object in motion. They are like separate films for a cinematograph; the great difficulty is to get them in their right sequence and make them pass in procession before the inner eye. If we could manage to do this and obtain the right sequence for a moment, then we should get in touch with some real living ideas. But the right grouping of the symbols is essential. However, the more we practise, the better we guess, the faster will the real ideas come. It is perhaps the greatest of arts-the true practice of the / Page 187 / art of symbolism. We can do it with our minds, with our eyes, with our bodies. Indeed if we could act this continuity between symbols, we should, it is said, breathe in ideas with every movement of the essential body; but this is far more difficult than practising with our minds.
Of course all this applies only to true symbols; many things called symbols are distorted or false appearances. No signs, no symbols, are worth anything unless they signify facts; that is to say, unless they represent transformations which will be experienced when inner vision develops.
A true symbol is something capable of containing life. It is never of any arbitrary shape. It must be, or it will never convey living ideas. Symbols, I believe, are not given to make us think in the ordinary sense; their main use is to convey life to our life and bring about a union. Their real use is to convey life of such power that it is capable of actually making an impression, or depression, upon the substance with which the higher mind is connected. They are the link between thought and action. Symbolism is connected with sigils, signatures, characters, types, in their root-meanings, with all the nomenclature connected with the impression of ideas on substance.
Before a man is capable of causing his subtle / Page 188 / substance to go through all these transformations, * or metamorphoses, at which we have hinted, before these' initiations '-beginnings or startings-can really take place in the rootmatter of his vehicles, it is possible for the transformations actually to take place in symbol in his higher mind of ideation. And this is a very desirable thing. To accomplish it in body is doubtless possible for a few only; but to accomplish it in mind is possible for many more. It is not dangerous, and it is a great developer of mental capacity.
It is a method of contemplation. The symbollearner should strive to get the mind quite still; to get the idea of the mind being as it were a sea of subtle substance. He must not think discursively; must not space out separatE.? symbols and look at them one after the other; but try to 'feel' the mind-substance being moulded.
Page 189
If, for instance, he think of 'potter' and , clay,' he should try to imagine the substance of the mind being moulded from one to the other continuously backwards and forwards, and watch them grow within himself. When practising symbols we should never' objectivise' or project; we should rather' feel' them grow within, and then an occasional idea may flash through.
It is, however, not desirable to pay too much attention to these ideas, for noticing them immediately transfers the consciousness to another' plane' of mind; for though this practice is a mental one it is not in itself a , science.' It is better to notice the ideas that flash forth just sufficiently to record them on the memory-plate, so that they can be used later when the tranquillity of mind that is the essential condition of the practice, has been left.
The world-body, or great surround, or essenceenvelope, of every man may be thought of as, so to speak, the L.C. M., or rather G.C.M., of all symbols. It is a useful practice to play with spheres and circles and conic sections, and so try to get ideas along these lines. It is quite credible that it is possible to resolve every symbol into an 'attitude,' so to say, or 'action,' or rather' activity,' of this world-body, and / Page 190 / so connect and link up all symbols by means of this world-soul, which is soul and body also.
This world-body may be said to be our way out of manhood into the cosmos; and so also is the art of symbolism the way out of men's language into the language of the gods. Rootsymbols may be regarded as fundamental lines and curves which carry with them certain powers and certain meanings, and these lines and curves are to be found in every science and art of men. They are, from this standpoint, the roots from which all sciences and arts grow, the foundations on which they are built, the gates forth to greater worlds.
It is not, however, to be supposed that such symbolism is the end of the matter; by no means. It is introductory to the linking of Mind on to this world-body. Symbols are, so to say, snapshots of the self-motivity of this world-body; they teach concerning its breathing, concerning the pulsing of its heart.
And even as we can get from art to science or gnosis by means of symbols, so can we get from mind to mind and from Person to Person, - not personality, but the Higher Person or Mind.
But this world-body does not mean a mass of some vast size. This world-body has no definite size; it breathes and is a different size for every mode of breath. It is a node, rather. It is an / Page 191 / ' atom' ordered according to the greater cosmos; and in the greater cosmos the mystics say all things are the same size, or all things are any size, or, again, there is no such thing as size. It does not count in the greater consciousness, any more than we think of the' size' of our breath; though from another point of view, mystically considered, the objective worlds of size are in the breath of the Gods; they breathe and the worlds act, but the Gods do not consider their size.
It might thus be said that every man's worldbody is the same size. They are all exactly alike; each is an 'atom,' each is a scale. It is our Great Person or Higher Self that decides what key the scale is in. This means that our Divine Word relates our group of 'letters,' or ' sounds,' or 'planets,' on to something further, and gives them a peculiar meaning of their own. Yet every world-body consists of the same letters, the same groups of sounds, otherwise the Holy Confraternity would be an impossibility.
All this is intimately connected with the mystery of Spirit or Divine Breath; so that when a man's mind is capable of being' fired' with Spirit, it can immediately mould and form
his substance into symbols. It is this power of continually forming man's substance into symbols which brings with it the power of understanding, / Page 192 / for symbols may be said to be the link between substance and Spirit.
It should be noted in this connection, that this language of symbols does not teach us about reincarnation; it is not on that side of things, and this interpretation cannot be forced upon it. Reincarnation is connected with the mind of man, and can be talked about in words; symbols depict the activities of Life in the man's world-body, and are not concerned with death, or form in activity, and the experiences of little persons.
Symbols have rather to do with that which is aeonian, or age-long. A true symbol must be of world-wide experience and age-long experience; it must not be local or temporary.
Thus the only way to control the proteus of symbolism is by becoming him, and so keeping pace with every change, transformation, or metamorphosis; and if one is not as yet strong enough to grip the heart of the matter, at any rate it is something to know the futility of trying to get a true hold by grasping at this or that fleeting appearance.
Page 188. Notes. * The earliest redactor of the Naassene Document writes: "And the Chaldreans say that Soul is very difficult to discover and hard to understand; for it never remains of the same appearance, or form, or in the same state, so that one can describe it by a general type, or comprehend it by an essential quality." On this the Church Father Hippolytus comments, referring to the Naassenes, or Disciples of the Serpent of Wisdom: "These variegated metamorphoses they have laid down in the Gospel superscribed 'According to the Egyptians.''' (See Thricegreatest Hermes, i. 150.)
NAASSENE 51111555 NAASSENE
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
J |
K |
L |
M |
N |
O |
P |
Q |
R |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
1+0 |
1+1 |
1+2 |
1+3 |
1+4 |
1+5 |
1+6 |
1+7 |
1+8 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
S |
T |
U |
V |
W |
X |
Y |
Z |
I |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
9 |
1+9 |
2+0 |
2+1 |
2+2 |
2+3 |
2+4 |
2+5 |
2+6 |
ME |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
= |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
18 |
9 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
1+8 |
= |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
9 |
= |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
1 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
9 |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
I |
ME |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
14 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
19 |
10 |
1 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
19 |
10 |
1 |
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
14 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
19 |
10 |
1 |
- |
- |
|
- |
9 |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
2+5 |
- |
|
|
9+7 |
5+2 |
2+5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
1+6 |
- |
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
14 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
1 |
- |
1 |
|
59 |
32 |
5 |
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
14 |
5 |
5 |
|
= |
5 |
- |
1 |
|
5 |
5 |
5 |
- |
- |
|
- |
9 |
|
|
|
|
- |
|
2+5 |
- |
|
|
9+7 |
5+2 |
2+5 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
1+6 |
- |
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIGHT 56-29-11-2-11-29-56 LIGHT
ISIS 56-20-2-2-56 ISIS